We already know that JavaScript is a client-side scripting language which runs on Web browsers thanks to the JavaScript Engine enabled within them. But the usage of JavaScript is not only limited client-side scripting anymore, rather it could be utilized in server-side to create effective, robust web applications.

Node.js is JavaScript runtime environment which implements JavaScript outside of a web browser. This aims in creating dynamic web applications and delivering them onto client web browsers. Just like JavaScript, Node.js also implemented using Non-blocking I/O, which makes for much faster and effective web application development.
History
Node.js was first introduced in 2009 by Ryan Dahl.
Main languages behind Node.js
The V8 engine, where node.js is being executed is built by using C++. Other than that C and ofcourse, JavaScript has been used in building Node.js.
What is Cool about Node.js
Node.js growing high in demand. It is now being used by many popular corporate organizations such as Microsoft, IBM, Netflix, IBM, Yahoo, Walmart etc. The success behind this fast growth of popularity could be listed down to the following attributes.
- Fast
- Scalable
- Increased Throughput
- could be used real-time applications
How Node.js is Working
Node.js allows the creation of Web servers and networking tools using JavaScript and a collection of “modules” that handle various core functionality.
In server-side languages such as PHP or Ruby, most functions are handled one at a time (when one function is executing, other functions have to wait till their turn). But in Node.js functions are being executed using non-blocking I/O mechanisms which enables running multiple functions parallely.
How Node.js handles requests?
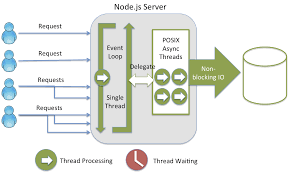
Unlike other server-side appilications, Node.js is single-threaded. But by employing Non-Blocking I/O (Also Known as Asynchronous I/O) where in this case a particular request can start its execution without waiting for a termination of a process which started earlier. This process is accommodated by an Event loop and each function performing I/O must use a callback. This mechanism allows for processing multiple requests at a given time thus enhancing the overall performance of the web application implemented using Node.js.
NPM

NPM (Node Package Manager) default package manager for Node.js. This contains all the related modules, packages that will make development much faster and efficient while managing the dependencies among Node.js packages.
Node Basics…
Under this topic, I am going to share some of the node basics I employed on my practice programs and will give a brief description about each feature.
Before going through my work, first I would explain some of the basic concepts in Node.js.
Module
Node module is simply a reusable piece of code. You can use modules anywhere in your code using the require keyword. There can built-in modules and as well as you can create your own custom modules as well.


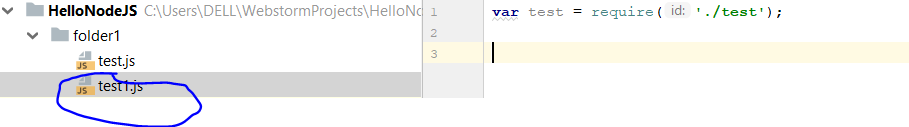
Note : ./ is used while requiring custom modules.
Creating Server-side web application by Node.js using Express
Express.js is a very popular framework used for creating web applications in Node.js. This framework really facilitates creating fast and effective web applications by utilizing its various modules provided.
For the following examples, I am going to be using Jetbrains Webstorm IDE.
Step 1 : Create a Node.js Express App

Under options, you can select any template you want. I am going to be using EJS (Extended JavaScript).

Little bit about the Project Structure…
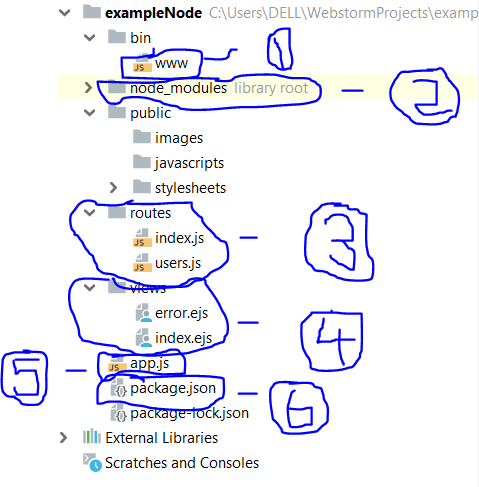
- bin/www – This is the startup file of your project. Which means in order to run your project in the web browser, you need to run this file.

after running bin/www, type localhost:3000 on your web browser and you will see something like this.

Displaying your Node.js express app on your browser
2. node_modules – contains all the necessary libraries for the application.
3. routes – you have define the path to each resource (page) in your application under this directory. In this case, index.js contains the path for the index.ejs as follows.
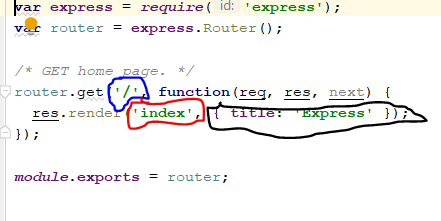
Here. we have imported the express module using require and then have used an instance of its Router class using Router() method. router.get() is used for HTTP requests which uses the GET method. First parameter which is encircled by blue color indicates the format of the URL. Second parameter is a callback function where inside the function you define the route for the relevant target. In this case index.ejs is the page we want the route for. (we do not want to use .ejs extension explicitly because the system already knows the extension). Then finally we made to available to be accessed by other files, using module.exports.
4. views – Basically contains the pages that we see through the browser. The content is almost the plain HTML, but you can use implement JavaScript as well.
5. app.js – This file is responsible for handling all the routing inside the application. Also this is the most important file of your application. bin/www loads this file so that from there onwards app.js can carry out its work.

6. package.json – This file contains all the relevant dependencies which need to be installed when creating a new project.
My own experience with Node.js
Upto now I have been discussing simply what Node.js is all about. Now I will focus on few things I tried using Node.js with Express. Let’s start with the Home Page.

As you can see, there are 3 links appearing in the home page : Home, About Me and No link (I didn’t assign any link to “No Link” 😦 ). This is how the corresponding HTML looks like.

The hyperlinks in the page are in a different page called header.ejs which is located inside a folder called templates and it can be included inside any page using include.The area encircled in black contains some of the variables passed into the Home.ejs. But how did I pass those variables here?

In here, the area encircled in black is a JavaScript object which is being passed onto index.ejs. In index.ejs you can access the properties of that object (in this case “title”).

Let’s see how this view is implemented…

As you can see I have included some list items inside a forEach loop where it displays some ID and a name. For the ID, I have given a hyperlink as well. Let me show you what I did there.
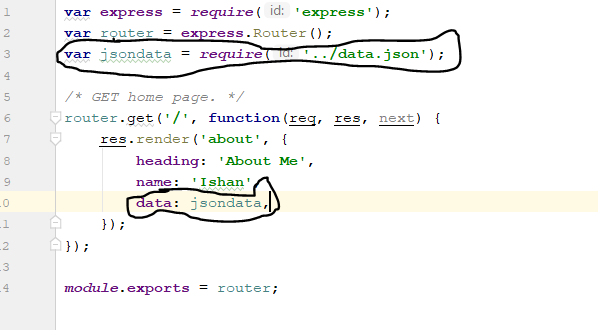
What I have done here is that I imported some JSON data and included that inside JavaScript Object which is to be passed to about.ejs. Image given below shows the actual data inside the JSON file.

Next I will show you what happens after I click on ID link in the “About Us” Page…
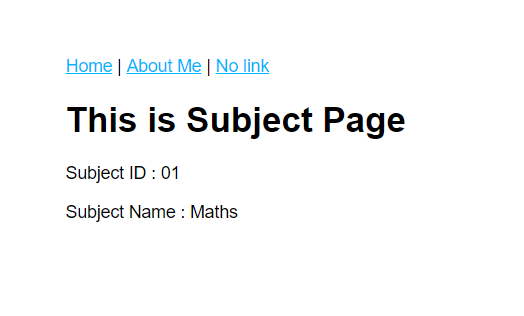
Initailly when I clicked on subject ID 01, that ID and the subject name getting passed using query string and those two attributes could be displayed in the “subject” page as above. Here is the HTML behind this page.

The corresponding js file is shown below…

To access the Query String variables, you need to use req.query.variable_name.
What If I want to Add another page into the Application?
To answer this question. I am going explain how I added “About Me” page.
Step 1 : Create the view for your page inside the “views” directory (about.ejs).
Step 2 : Create the corresponding js file inside the “routes” directory (about.js) to implement the routing method for the new page.
Step 3 : Add a reference to your new page in the app.js file as follows.

Step 4 : Introduce a middleware to the new page.
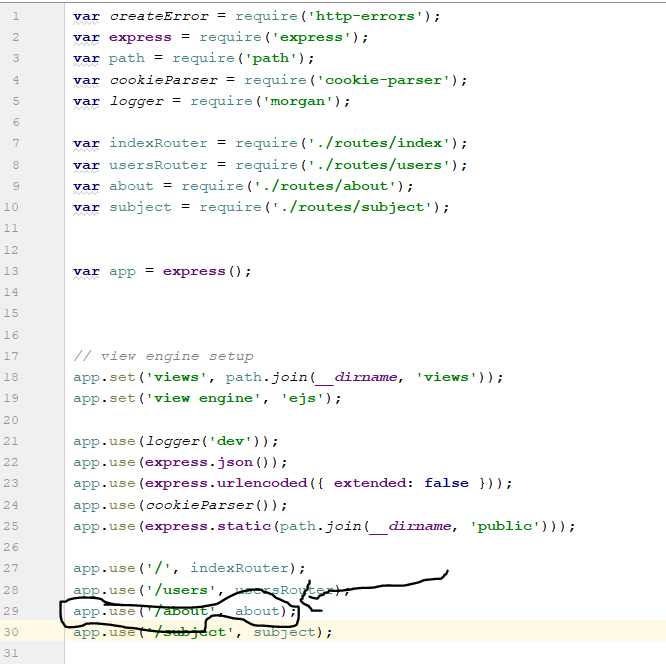
Creating a middleware for the new page
That’s all you have to do add a new page!!!!
So in this section I talked about what Node.js is all about, why is it so popular, how it works and finally shared some of my own work…That’s pretty much all I am going to talk about Node.js right now.
Coming Up Next…..
In the next chapter I will be exploring a bit about React.js and few things I found about it. As usual I will talk about what I Implemented using this wonderful piece of technology….